In an era marked by significant environmental and social challenges, the imperative for sustainable finance is not only evident but vital. These pressing issues threaten not just the natural ecosystems but the very fabric of our economic stability and human well-being. As we navigate through these turbulent times, sustainable finance emerges as a transformative strategy that integrates environmental, social, and governance ("ESG") considerations into financial services, thereby navigation investments towards long-term environmental stewardship and societal benefits.
1. Why Sustainable Finance is a Trend Right Now?
Market Demand and Investor Preferences
In recent years, there has been a remarkable shift in investor preferences toward sustainability. The driving force behind this shift is the growing recognition that sustainable investments can provide competitive returns while also mitigating risks associated with ESG issues. Investors are increasingly demanding that their capital not only yield financial returns but also contribute positively to societal goals. This demand has encouraged a significant increase in the allocation of funds to ESG-focused assets. According to Bloomberg, ESG assets are on track to exceed $53 trillion by 2025, representing more than a third of the projected $140.5 trillion in total global assets under management (Bloomberg, 2021).
Regulatory Push
Governments and international bodies are intensifying their focus on climate change and sustainability, which has led to an increase of regulations and standards aimed at promoting sustainable finance. The European Union, for example, has been particularly proactive with its Sustainable Finance Action Plan and the Green Deal, setting ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions and enhance sustainability reporting and investment transparency. These regulatory frameworks compel companies and financial institutions to integrate sustainability into their operations and reporting processes, driving the trend toward sustainable finance.
Technological Advancements
The advancement of technology has facilitated the growth of sustainable finance by improving access to data and the ability to analyze it. Enhanced data analytics and artificial intelligence are being used to assess ESG metrics accurately, thereby enabling investors to make more informed decisions. Technologies are also emerging as tools for improving the transparency and traceability of sustainable investments, ensuring that funds are used appropriately and effectively.

Societal Awareness and Consumer Behavior
There is a growing societal awareness of environmental and social issues, driven by global challenges such as climate change, resource depletion, and social inequalities. This awareness has changed consumer behavior significantly, with more individuals seeking out products and services from companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. As consumers become more environmentally and socially conscious, businesses are responding by embedding sustainability into their core strategies to maintain competitiveness and relevance in the market.
Financial Performance and Risk Management
Empirical evidence increasingly supports the notion that companies with robust sustainability practices perform better financially and exhibit lower volatility than their less sustainable counterparts. Sustainable companies are often better positioned to manage risks related to environmental regulations, social unrest, and governance scandals. Moreover, as the physical impacts of climate change become more apparent, companies prioritizing sustainability are likely to face fewer operational disruptions and financial liabilities.
Global Collaboration and Standardization
The trend toward sustainable finance is also being propelled by increased global collaboration and the standardization of sustainability metrics. International coalitions and frameworks, such as the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures and the Global Reporting Initiative, provide guidelines that help unify the approach to measuring and reporting on sustainability. These efforts facilitate cross-border investments in sustainable projects and enhance global cooperation in addressing common challenges.
2. Why Sustainable Finance is Indispensable?
The call for sustainable finance resonates more profoundly today than ever before. Our planet struggles with the severe consequences of unchecked industrial growth such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and severe pollution. These pressing issues threaten not just the natural ecosystems but the very fabric of our economic stability and human well-being.
As highlighted by the European Commission, sustainable finance is essential for "supporting economic growth while reducing pressures on the environment and contributing to the creation of a climate-neutral economy" (European Commission, 2020). This delicate balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability is key to securing long-term prosperity.

3. Mutual Responsibilities
in Advancing Sustainable Finance.
In the evolving landscape of sustainable finance, both banks and their customers face distinct expectations designed to foster a collaborative environment conducive to achieving sustainability goals
Incorporating Sustainability in Global Transaction Banking ("GTB")
For banks, the transition involves assuming a leadership role in integrating ESG principles into their core operations. This includes not only offering products that support sustainable initiatives, such as green bonds and ESG-focused portfolios but also ensuring transparency in how their operations impact sustainability goals. Enhanced risk management strategies that incorporate ESG factors are becoming essential, alongside ongoing efforts to innovate and develop new sustainable financial tools and mechanisms. According to Bloomberg, the combined volumes of sustainability-rated debt instruments have expanded by approximately 80% per year, surging from about $155 billion in 2017 to over $1.6 trillion in 2021 (Bloomberg, 2021). This rapid growth underscores the increasing prioritization of ESG factors in investment decisions, reflecting a broader market trend towards sustainability in finance.
Despite this growth, the adoption of sustainable features within traditional GTB products has been comparatively slow. Many banks have only begun to scratch the surface of integrating sustainability measures into their offerings. The complexities arising from multi-party, paper-intensive processes and the lack of reliable data on companies’ sustainability activities pose significant challenges. However, with strategic adjustments and technological enhancements, these hurdles can be overcome to tap into the enormous potential of sustainable GTB.
The demand for sustainable GTB products is particularly strong in regions like the United States and Europe, where requests for proposals for trade finance projects involving sustainability criteria are rising. This growing demand is projected to significantly expand the revenue pools for sustainable GTB, with estimates suggesting that global revenue from sustainable GTB could reach between $28 billion and $35 billion by 2025. This represents a substantial increase, accounting for approximately 8% of the total global transaction banking revenue from core products (McKinsey, 2021).
"The revenue opportunity in sustainable global transaction banking (GTB) is estimated to grow to $28 billion–$35 billion by 2025."
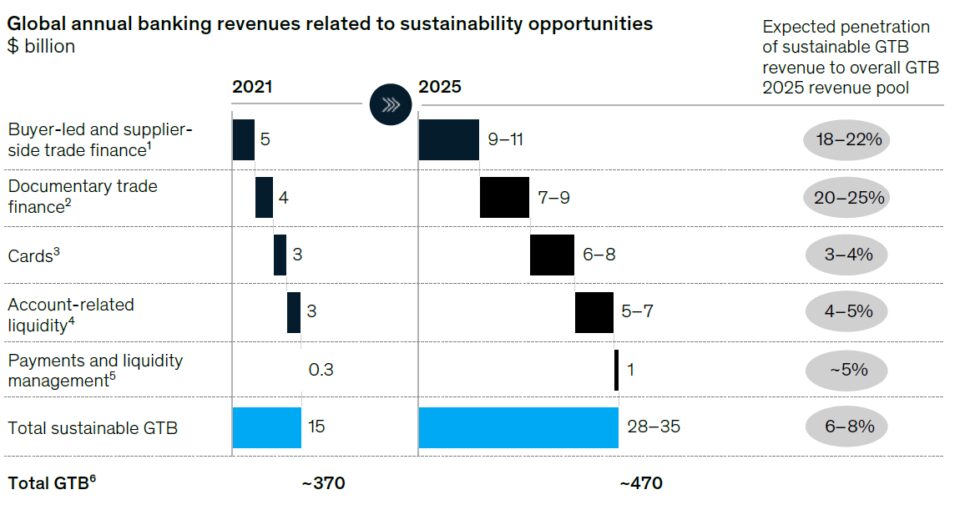
Incorporating Sustainability in Global Transaction Banking ("GTB")
Customers are encouraged to actively engage with sustainable financial products and to incorporate responsible practices into their own business operations. This includes making investment decisions that consider long-term environmental and societal impacts and advocating for broader access to sustainable finance options. Through responsible consumption and a commitment to sustainability principles within their investment and operational decisions, customers can significantly influence the pace and breadth of sustainability initiatives undertaken by financial institutions.
Together, these responsibilities underline the cooperative relationship between financial institutions and their clients, emphasizing the collective effort required to steer the global economy towards more sustainable outcomes. As both banks and customers navigate this terrain, their actions will collectively contribute to the broader goals of environmental conservation, social equity, and economic stability.
4. The Tangible Benefits of Sustainable Finance
- Economic Stability and Growth: Investing in sustainable enterprises not only yields substantial long-term returns but also diminishes the financial risks associated with environmental degradation. Projects like green buildings and renewable energy not only conserve the environment but also stimulate local economies through job creation.
- Corporate Reputation and Consumer Trust: Companies at the forefront of sustainable practices gain a distinct competitive advantage. This enhanced reputation attracts conscientious investors, consumers, and employees, aligning with the growing trend of making choices based on ethical considerations and social responsibility (Harvard Extension School, 2020).
- Regulatory Compliance and Innovation: Adhering to stringent environmental regulations, such as those outlined in the EU’s Action Plan on Financing Sustainable Growth, companies mitigate risks and align themselves with global climate commitments. This compliance fosters innovation, particularly in green technologies, opening new avenues for business growth (European Commission, 2020).
Conclusion
The shift towards sustainable finance is a compelling narrative of adaptation and responsibility. It represents a fundamental change in how the financial industry operates, underscoring the need for an approach that is not only economically viable but also responsible to society and the environment. As we look towards the future, the financial sector’s commitment to sustainable development will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping a resilient, prosperous, and environmentally conscious global economy.
At GBI, as a member of the BBVA Group, we are committed to supporting sustainable finance initiatives. Should you have any inquiries or need assistance in exploring these opportunities, we are here to help guide and support your efforts in sustainable finance.

References
- European Commission. (2020). Overview of sustainable finance.
- Harvard Extension School. (2020). What Is Sustainable Finance and Why Is It Important?
- BloombergNEF. (2021). ESG assets may hit $53 trillion by 2025, a third of global AUM.
- McKinsey & Company. (2021). Sustainability in global transaction banking: A market imperative.



